A new Filtering Algorithm for Medical Magnetic Resonance and
Computer Tomography Images
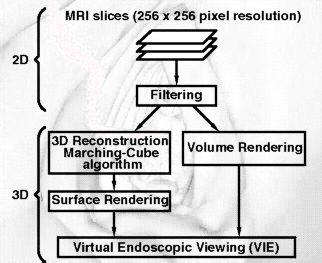 Inner views of tubular structures based on Computer Tomography (CT) and
Magnetic Resonance (MR) data sets may be created by virtual endoscopy.
After a preliminary segmentation procedure for selecting the organ to
be represented, virtual endoscopy is a new post processing technique
using surface or volume rendering. In case of surface
rendering, the segmentation is based on a grey level thresholding technique.
To avoid artifacts due to the noise created in the imaging process,
and to restore spurious resolution degradations, a robust Wiener filter
was applied. This filter working in Fourier space approximates the noise
spectrum by a simple function that is proportional to the square root
of the signal amplitude. Thus, only points
with tiny amplitudes consisting mostly of noise are suppressed.
Further artifacts are avoided by the correct selection of the
threshold range.
Inner views of tubular structures based on Computer Tomography (CT) and
Magnetic Resonance (MR) data sets may be created by virtual endoscopy.
After a preliminary segmentation procedure for selecting the organ to
be represented, virtual endoscopy is a new post processing technique
using surface or volume rendering. In case of surface
rendering, the segmentation is based on a grey level thresholding technique.
To avoid artifacts due to the noise created in the imaging process,
and to restore spurious resolution degradations, a robust Wiener filter
was applied. This filter working in Fourier space approximates the noise
spectrum by a simple function that is proportional to the square root
of the signal amplitude. Thus, only points
with tiny amplitudes consisting mostly of noise are suppressed.
Further artifacts are avoided by the correct selection of the
threshold range.
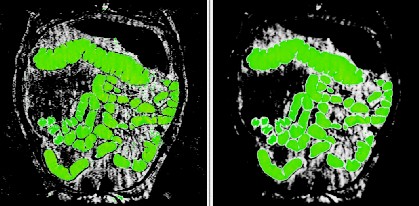
The segmentation process is demonstrated on a MR-colonography
slice in coronal plane (left hand side figure) before and (right hand
side figure) after the application of the new filtering algorithm.
Green picture segments have intensity values larger than the chosen
threshold and white picture segments are the reminder points due
to noise and background intensities created by other organs.
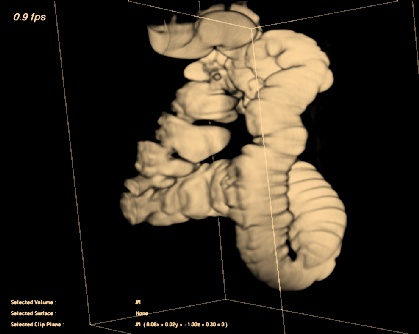
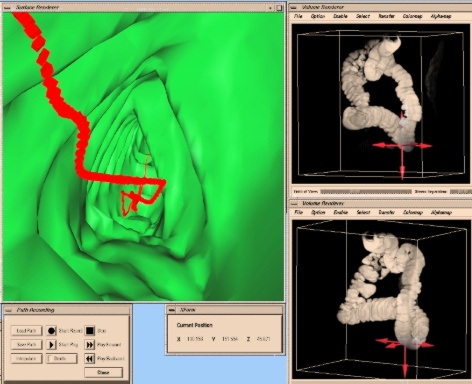 After the filtering and thresholding process, the lumen and the inner walls
of the tubular structures are well represented and allow one to distinguish
between harmless fluctuations and medically significant structures.
After the filtering and thresholding process, the lumen and the inner walls
of the tubular structures are well represented and allow one to distinguish
between harmless fluctuations and medically significant structures.
For more information see:
A new filtering algorithm for medical magnetic resonance and
computer tomography images
Erich Stoll,
Christian
Stern,
Peter
Stucki, and
Simon
Wildermuth
Journal of
Digital Imaging, 12, #1, 23 (1999).
A recent study in New England Journal of
Medicine, 349, 2191-2200 (2003), Computed Tomographic Virtual Colonoscopy to Screen for Colorectal Neoplasia in Asymptomatic Adults, of Perry J. Pickhardt et al has
shown that virtual endoscopy is more reliable for early
recognition of colon cancers than usual optical endoscopy.




